

Welcome!
- We are here for you!
- Every question is important
- Help each other
- Have fun
- Feel free to take a break whenever you need one!
Our Sponsors

Why is it called BitCamp?
A bit (short for binary digit) is the smallest unit of data in a computer. A bit has a single binary value, either 0 or 1.
youtube.com/madewithcode
What is software?
Computer Instructions
What kind of stuff uses software?
Smartphones & Mobile Apps


Fitness Trackers
Thermostats

Self-driving Cars

What kind of stuff does
a software developer do?
Software Developer = Master Builder





Master Builders
solve problems
build cool things
use their imagination
All things software developers get to do every day
Being a Software Developer...
is like being paid to be creative, solve problems, and build things.
Questions?
Software Languages

Software Languages

What is HTML?
HTML is the code that allows us to build websites
HyperText Markup Language

Terms
-
Web designThe process of planning, structuring and creating a website
-
Web developmentThe process of programming dynamic web applications
-
Front endThe outwardly visible elements of a website or application
-
Back endThe inner workings and functionality of a website or application.
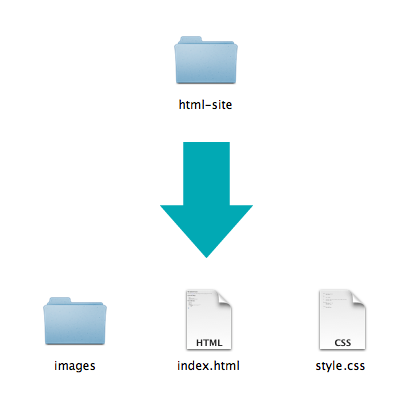
Get Started: Folder Structure
All the files for your site should be stored within the same folder.
This includes:
- HTML Files
- CSS Files
- Images
- Script files
- Anything else that will appear on your site
Note: File names should not include spaces or special characters. File names ARE case sensitive.
Let's develop it!
Let's set up our folder structure and create files.
Next we'll get started on our site!
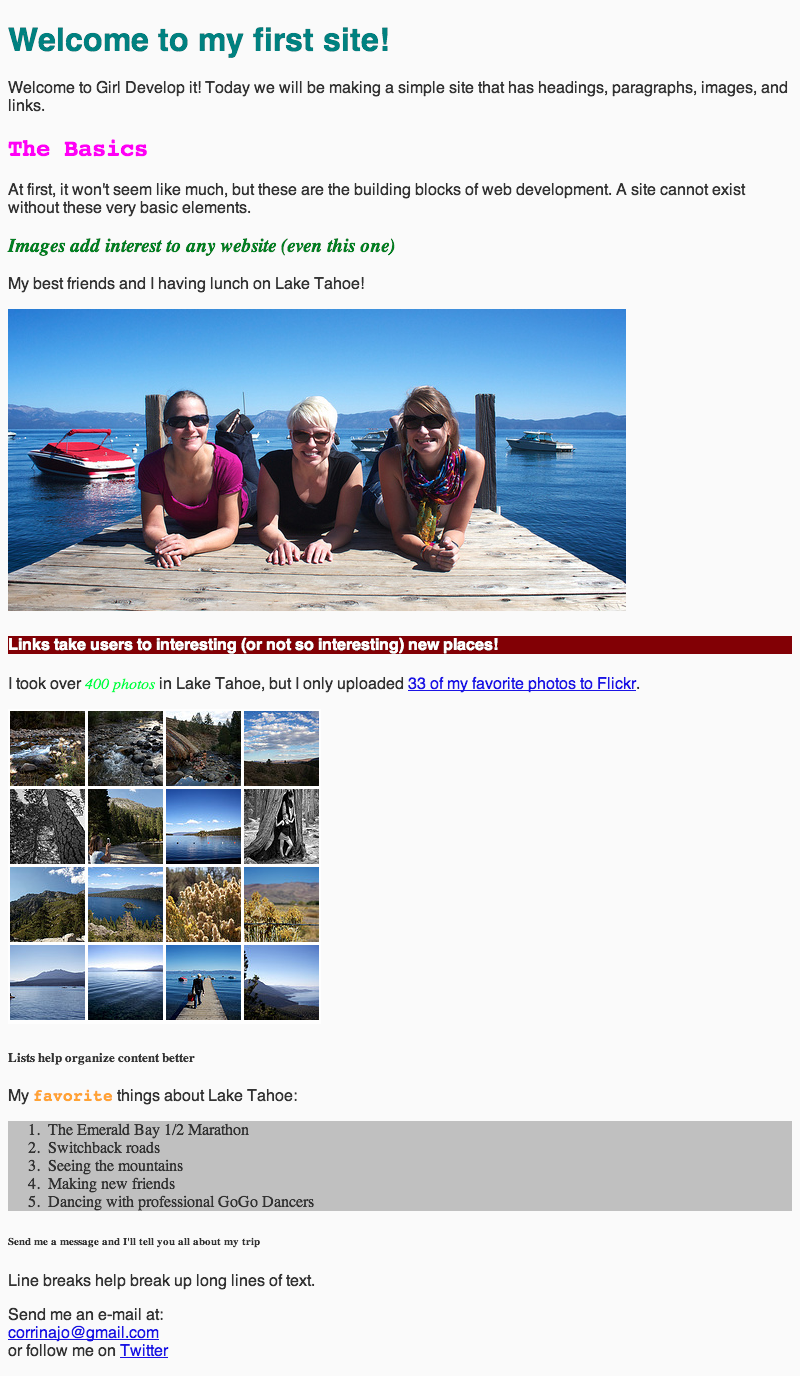
What we'll be building today
Today we will be learning how to code a site from scratch using paragraphs, headings, links, images, and lists.
Did you know...
...that you can see the code of any website?
Right click
=> "View page source"
or
 (Options)
(Options)
=> More Tools
=> Developer tools
Anatomy of a website
A website is a way to present your content to the world, using HTML and CSS to present that content & make it look good.
Anatomy of a website
-
A paragraph is your content
- Putting your content into an HTML tag to make it look like a paragraph is Structure
<p>A paragraph is your content</p>Anatomy of an HTML element
-
Element
- An individual component of HTML
- Paragraph, heading, table, list, div, link, image, etc.
-
Tag
- Marks the beginning & end of an element
- Opening tag and Closing Tag
- Tags contain characters that indicate the tags purpose
<tagname>Stuff in the middle</tagname><p>This is a sample paragraph.</p>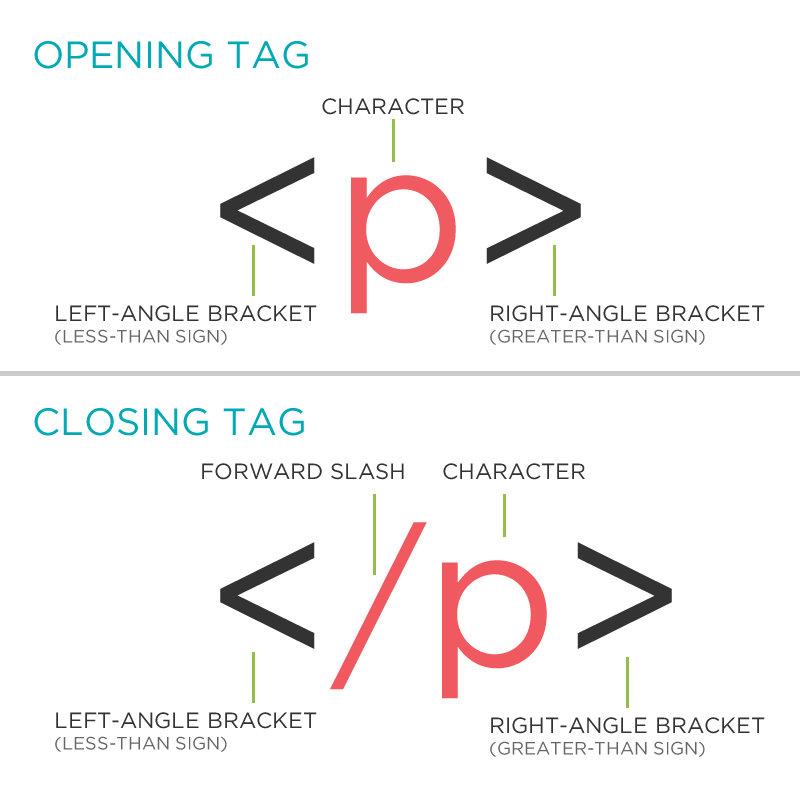
Anatomy of an HTML element
-
Container Element
- An element that can contain other elements or content
- A paragraph (<p>) contains text
-
Stand Alone Element
- An element that cannot contain anything else
<br/>
<img/>
Anatomy of an HTML element
-
Attribute
- Provides additional information about the HTML element
- Class, ID, language, style, identity, source
- Placed inside an opening tag, before the right angle bracket.
-
Value
- Value is the value assigned to a given attribute.
- Values must be contained inside quotation marks.
<div id="copyright">© GDI 2013</div>
<img src="my_picture.jpg"/>
<a href="http://girldevelopit.com">GDI</a>
Doctype
The first thing on an HTML page is the doctype, which tells the browser which version of the markup language the page is using.
<!DOCTYPE html>* The doctype is case-insensitive.
DOCtype, doctype, DocType and DoCtYpe are all valid.
HTML Tag
After <doctype>, the page content must be contained between <html> tags.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
</html>
Head and Body Tags
- Contains the page title & meta information about the page.
-
Meta information is not visible to the user, but contains helpful information about the site.
- Tells search engines about your page and who created it
- Provides a description of your site
- Contains the actual content of the page.
- Everything contained in the body is visible to the user.
Head and Body Tags
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>My Awesome Site</title>
</head>
<body>
Best page content ever!
</body>
</html>
Let's develop it!
Let's get our web page set up with a doctype, head, title and body.
Later we'll add some content to it!
Nesting
All elements "nest" inside one another

Whichever element OPENS first CLOSES last
Nesting: Example
Elements are 'nested' inside the <body> tag.
<body>
<p>A paragraph inside the body tag</p>
</body>
Paragraphs 'nested' inside list items.
<ul>
<li>
<p>A paragraph inside a list item</p>
</li>
</ul>
Element: Paragraph
<p>Paragraph 1</p>
<p>Paragraph 2</p>
<p>Paragraph 3</p>
<p>Paragraph 1</p> <p>Paragraph 2</p> <p>Paragraph 3</p>
<p>Paragraph 1</p>
<p>Paragraph 2</p>
<p>Paragraph 3</p>
Paragraph 1
Paragraph 2
Paragraph 3
* White space is only for humans!
Example: Paragraphs
Paragraphs allow you to format your content in a readable fashion.
* You can edit how paragraphs are displayed with CSS
Element: Heading
<h1>Heading 1</h1>
<h2>Heading 2</h2>
<h3>Heading 3</h3>
<h4>Heading 4</h4>
<h5>Heading 5</h5>
<h6>Heading 6</h6>
Heading 1
Heading 2
Heading 3
Heading 4
Heading 5
Heading 6
* Heading number indicates hierarchy, not size.
Example: Headings
Formatted text
<p>
Here is a paragraph with
<em>Emphasized</em> text and
<strong>Important</strong> text.
</p>
Here is a paragraph with Emphasized text and Important text.
* Note: These tags are meant for meaning, not style.
Let's Develop it!
Let's add some content to our site!
Add some...
- Headings
- Paragraphs
- Italic and bold text within paragraphs
Element: Link
Links have three components
- Tag: <a></a>
- Href attribute: "http://www.girldevelopit.com"
- Title attribute: "Girl Develop It"
<a href="http://www.girldevelopit.com" title="Girl Develop It">GDI</a>The <a> tag surrounds text or images to turn them into links
Link Attributes
Links can have attributes that tell the link to do different actions like open in a new tab, or launch your e-mail program.
<a href="home.html" target="_blank">Link Text</a>Link opens in a new window/tab with target="_blank"
<a href="mailto:info@girldevelopit.com">E-mail us!</a>Link opens mail program by inserting mailto: directly before the email address.
Relative vs. Absolute paths for links & images
-
Relative
- Relative paths change depending upon the page the link is on.
- Links within the same directory need no path information.
"filename.jpg" - Subdirectories are listed without preceding slashes.
"images/filename.jpg"
- Links within the same directory need no path information.
- Relative paths change depending upon the page the link is on.
-
Absolute
- Absolute paths refer to a specific location of a file, including the domain.
"http://www.girldevelopit.com/chapters/detroit"
- Absolute paths refer to a specific location of a file, including the domain.
- Typically used when pointing to a link that is not within your own domain.
Let's Develop It
Let's add links to our site!
Add links that...
- open in the same window
- open in a new window
- link to an email address
Element: Image
Images have three components
- Tag: <img/>
- Src attribute: "images/clydesdale.jpg"
- Alt attribute: "Horse"
<img src="images/clydesdale.jpg" alt="Horse"/>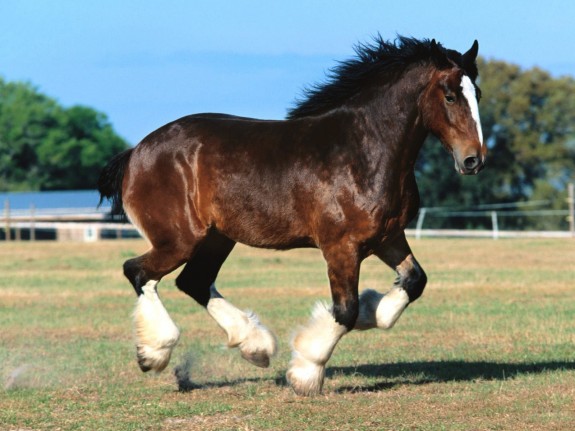
Element: Line Break
<p>
Everything is awesome <br/>
Everything is cool when you're part of a team <br/>
Everything is awesome <br/> When we're living our dream <br/>
</p>
Everything is awesome
Everything is cool when you're part of a team
Everything is awesome
When we're living our dream
Let's Develop It!
Let's add some images and line breaks to our page.
We can even turn our images into links!
Element: Unordered and ordered lists
<ul>
<li>List Item</li>
<li>AnotherList Item</li>
</ul>
<ol>
<li>List Item</li>
<li>AnotherList Item</li>
</ol>
Unordered list (bullets)
- List Item
- AnotherList Item
Ordered list (sequence)
- List Item
- AnotherList Item
Lists: Examples
Lists can be used to organize any list of items.
Comments
You can add comments to your code that will not be seen by the browser, but only visible when viewing the code.
<!-- Comment goes here -->
Comments can be used to organize your code into sections so you (or someone else) can easily understand your code. It can also be used to 'comment out' large chunks of code to hide it from the browser.
<!-- Beginning of header -->
<div id="header">Header Content </div>
<!-- End of header -->
<!--
<ol>
<li>List Item</li>
<li>Another List Item</li>
</ol>
-->
Tables
Tables are a way to represent complex information in a grid format.
Tables are made up of rows and columns.
<table>
<tr>
<th>Head</th>
<th>Head</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Data</td>
<td>Data</td>
</tr>
</table>
| Head | Head |
|---|---|
| Data | Data |
Tables: Examples
Tables can be styled with CSS to add zebra striping or to highlight important rows/columns.
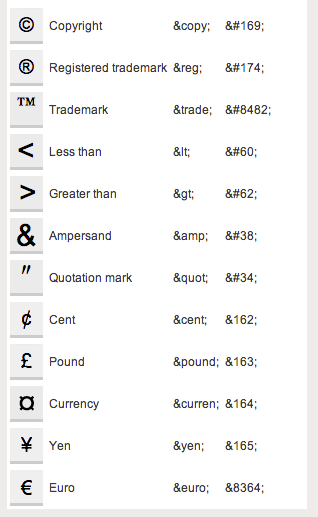
Character codes
There are character codes for many different characters in many different languages
- Delta: δ δ
- Copyright symbol: © ©
- Grave: ` `
- An grave a: à à
- A full list is available at htmlandcssbook.com
Questions?
Let's Develop it!
Let's add some...
- Ordered and unordered lists
- Comments
- Tables
We can make a list of links, a list of images, or a table of images!
Anatomy of a website
A website is a way to present your content to the world, using HTML and CSS to present that content & make it look good.
CSS: What is it?
CSS = Cascading Style Sheets
CSS is a "style sheet language" that lets you style the elements on your page.
CSS works in conjunction with HTML, but is not HTML itself.
CSS: What can it do?
All colored text, position, and size is created using CSS
CSS: What does it look like?

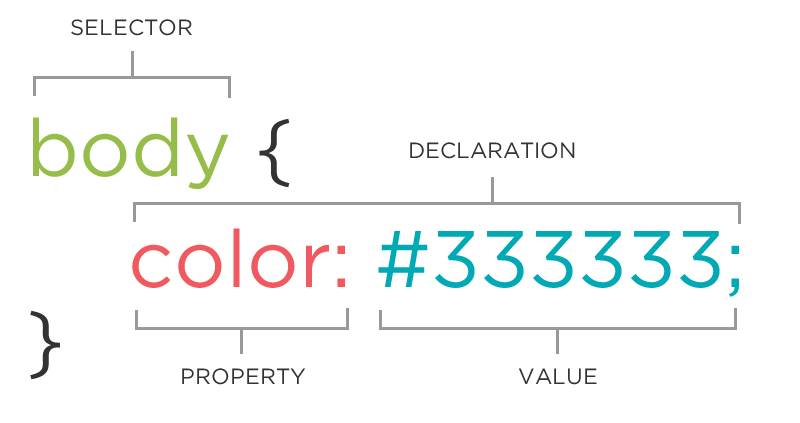
The CSS Rule
The CSS Rule
selector {
property: value;
}
A block of CSS code is a rule.
The rule starts with a selector.
It has sets of properties and values.
A property-value pair is a declaration.
CSS Syntax
Declarations: Property and value of style you plan to use on HTML element.
Declarations end with a semicolon.
Declaration groups are surrounded by curly brackets.
selector {
property: value;
property: value;
property: value;
}
Selector: Element
p {
property: value;
}
Selects all paragraph elements.
img {
property: value;
}
Selects all image elements.
Selector: ID
#footer {
property: value;
}
Selects all elements with an id of "footer".
<p id="footer">Copyright 2011</p>Selector: Class
.warning {
color: red;
}
Selects all elements with a class of "warning".
<p class="warning">Run away!</p>IDs vs. Classes
ex. A webpage only has one footer.
The "#" is how you tell CSS "this is an id."
ex. There can be many warning on one webpage.
The "." is how you tell CSS "this is a class name."
Selector: Position
p em {
color: yellow;
}
Selects all em elements that are within a paragraph
<p>This is <em>important.</em></p>Property: Color
The color property changes the color of the text.
p {
color: red;
color: #ff0000;
color: rgb(255, 0, 0);
}
Color name
Hexadecimal value
The 17 standard colors are: aqua, black, blue, fuchsia, gray, grey, green, lime, maroon, navy, olive, purple, red, silver, teal, white, and yellow.
Property: Background-color
The background-color property changes the color of the background.
p {
background-color: black;
background-color: #000000;
background-color: rgb(0,0,0);
}
Property: Font-family
The font-family property defines which font is used.
p {
font-family: "Times New Roman";
font-family: serif;
font-family: "Arial", sans-serif;
}
Specific font name
Generic name
Comma-separated list
Property: Font-size
The font-size property specifies the size of the font.
p {
font-size: 12px;
font-size: 100%;
}
Pixels
Percentage
Cascading
Styles "cascade" down until changed
p {
color:blue;
font-family: 'Helvetica';
}
.red {
color:red;
}
#special {
font-family: Arial;
}
<p>Paragraph</p>
<p class="green">Paragraph</p>
<p class="red">Paragraph</p>
<p class="red" id="special">Paragraph</p>
CSS Properties
Many CSS properties have self-explanatory names:
- color
- background-color
- font-size
- width
- height
Comprehensive list of all CSS properties:
https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/CSS/CSS_Reference
...or just Google it!
Connecting CSS to HTML
3 ways
"Inline"
"Embedded"
"External"
Connecting CSS to HTML: Inline
<p style="color:red">Some text.</p>Uses the HTML attribute style.
Difficult to use in large projects
Not preferred.
Connecting CSS to HTML: Embedded
<head>
<style type="text/css">
p {
color: blue;
font-size: 12px;
}
</style>
</head>
Inside <head> element.
Uses <style> tag.
Can only be used in one html file
Connecting CSS to HTML: Linked
<head>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css">
</head>
Shared resource for several pages.
Reduced file size & bandwidth
Easy to maintain in larger projects.
Questions?
Let's develop it
- Create a new .css file
- Add a link to the file in the head of the portfolio made last time
- Add styles to change the colors, background colors or fonts of different parts of your site
- Try using ids and classes to change specific elements